Volume of a solid of revolution
Another application of integral calculus is the calculation of the volume of a solid of revolution.
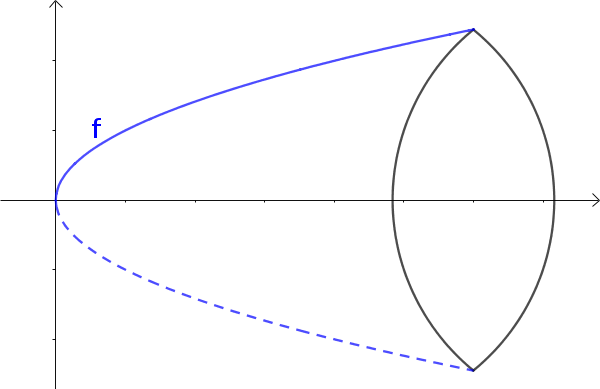
The solid of revolution is described by a function $f$ and rotates around the x-axis. The volume of the solid figure can be calculated with an integral.
The formula is
$V=\pi\cdot \int_a^b (f(x))^2\,\mathrm{d}x$
i
Method
- Square the function
- Insert and calculate integral
Example
The area under the function graph of $f(x)=\sqrt{x}$ rotates around the x-axis in the interval $[0; 6]$. Calculate the volume of the solid of revolution.
-
Square the function
Since $(f(x))^2$ occurs in the formula, you should do this for clarity beforehand.$(f(x))^2$ $=(\sqrt{x})^2$ $=x$
-
Insert and calculate integral
Insert the given limits of integration 0 and 6 as well as the squared function.$V=\pi\cdot \int_a^b (f(x))^2\,\mathrm{d}x$
$V=\pi\cdot \int_0^6 x \,\mathrm{d}x$
Determine definite integral$=\pi\cdot [\frac12 x^2]_0^6$ $=\pi \cdot 18$ $\approx56.55$
The volume is approximately 56.55 VU.
