Sine, Cosine and Tangent
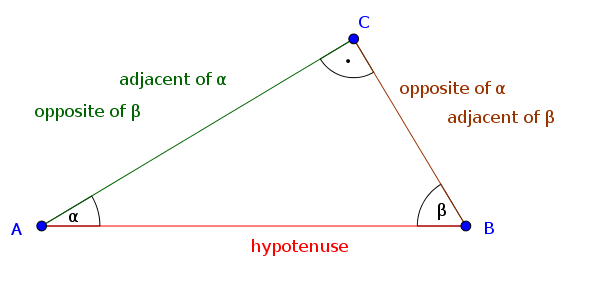
With Sine, Cosine and Tangent in each right-angled triangle, you can calculate the angle of the adjacent/opposite, or the angle itself, if two of the three quantities are known.
!
Remember
- Sine: $\sin=\frac{\text{opposite}}{\text{hypotenuse}}$
- Cosine: $\cos=\frac{\text{adjacent}}{\text{hypotenuse}}$
- Tangent: $\tan=\frac{\text{opposite}}{\text{adjacent}}$
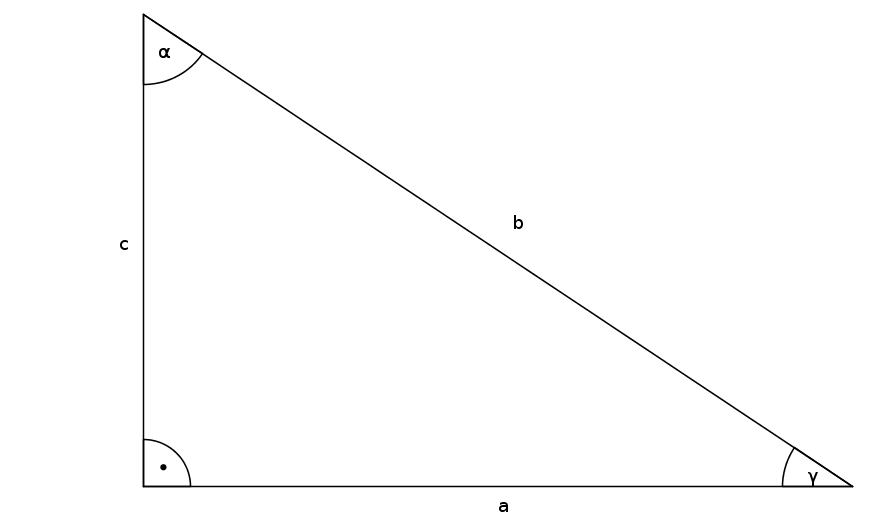
If you use the pages now, we find in our triangle ABC with $\gamma=90^\circ$:
- $\sin(\alpha)=\frac{a}{c}$ and $\sin(\beta)=\frac{b}{c}$
- $\cos(\alpha)=\frac{b}{c}$ and $\cos(\beta)=\frac{a}{c}$
- $\tan(\alpha)=\frac{a}{b}$ and $\tan(\beta)=\frac{b}{a}$
Example
Given is a right triangle with $\beta=90^\circ$, $\alpha=60^\circ$ and $c=4$. Calculate $b$.
Find the right formula
$\cos=\frac{\text{adjacent}}{\text{hypotenuse}}$
$\cos(\alpha)=\frac{c}{b}$Change the formula
$\cos(\alpha)=\frac{c}{b}\quad|\cdot b$
$\cos(\alpha)\cdot b=c\quad|:\cos(\alpha)$
$b=\frac{c}{\cos(\alpha)}$Insert and calculate
$b=\frac{4}{\cos(60^\circ)}=8$
