Law of sines
The sine rule is applicable in any triangle, if either
- one side and two angles or
- two sides and one angle are given.
In the second case, the angle must be opposite to one of the two given sides. Otherwise, you need the cosine rule.
!
Remember
In any triangle, two lengths are related to each other like the opposite sine values.
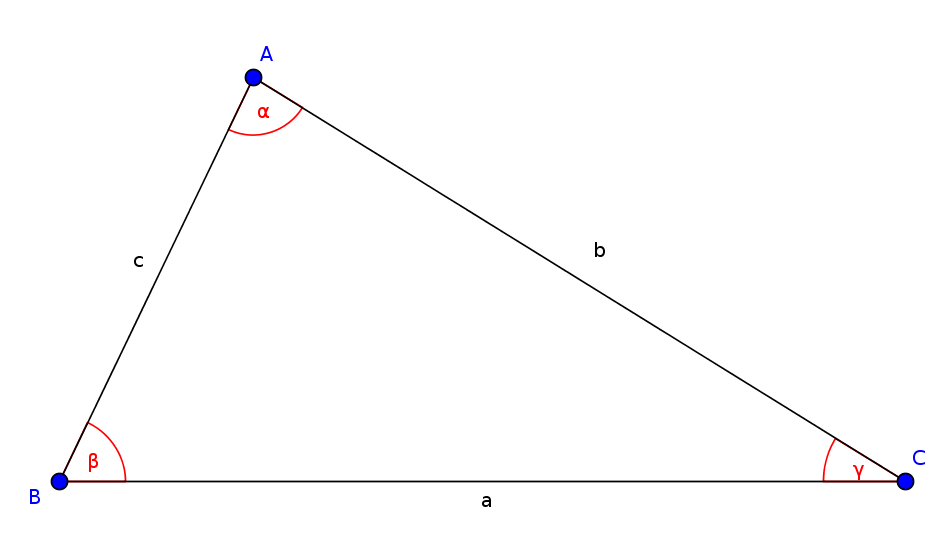
In our triangle ABC, the sine rule says:
- $\frac{a}{b}=\frac{\sin(\alpha)}{\sin(\beta)}$
- $\frac{b}{c}=\frac{\sin(\beta)}{\sin(\gamma)}$
- $\frac{c}{a}=\frac{\sin(\gamma)}{\sin(\alpha)}$
- $\frac{a}{\sin(\alpha)}=\frac{b}{\sin(\beta)}=\frac{c}{\sin(\gamma)}$
Example
Given is a triangle with $a=7$, $c=4$ and $\gamma=30^\circ$. Calculate the angle $\alpha$.
Find the right formula
$\frac{a}{c}=\frac{\sin(\alpha)}{\sin(\gamma)}$Change the formula
$\frac{a}{c}=\frac{\sin(\alpha)}{\sin(\gamma)}\quad|\cdot\sin(\gamma)$
$\sin(\alpha)=\frac{a}{c}\cdot\sin(\gamma)$Insert and calculate
$\sin(\alpha)=\frac{7}{4}\cdot\sin(30^\circ)$
$\alpha=\sin^{-1}(\frac{7}{4}\cdot\sin(30^\circ))\approx61^\circ$
