Linear and proportional growth
Linear growth
In the case of linear growth, the value $N(t)$ for the same period of time ($c$) is always added with the same addend ($d$)
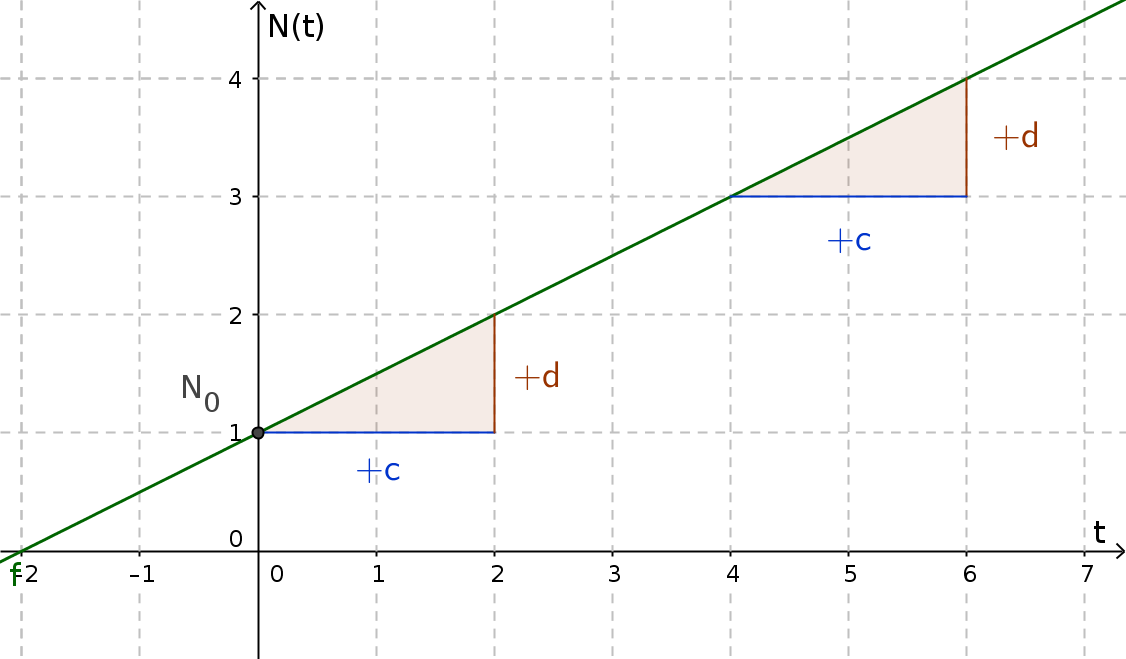
The general equation of linear growth is:
$N(t)=m\cdot t + N_{0}$
$t...$ Period of time
$m ...$ Growth factor
$N(t) ...$ Value in dependence on $t$
$N_{0} ...$ Initial amount/start value
Proportional growth
Proportional growth is like linear growth, but with an initial amount of 0.
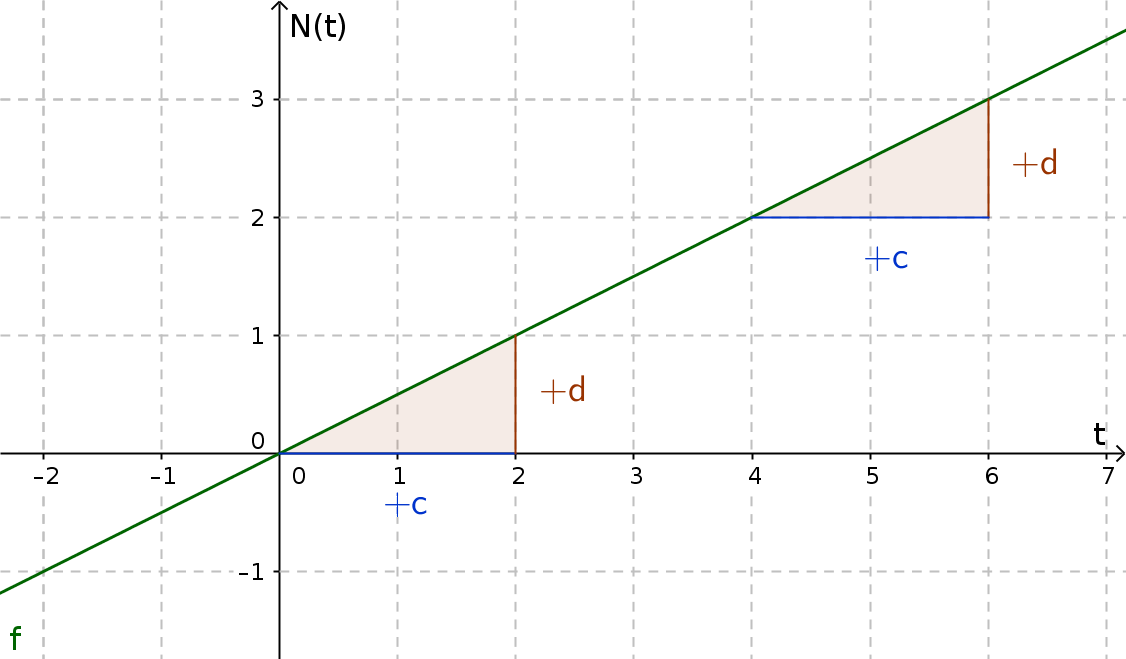
The general equation would be:
$N(t)=m\cdot t$
$N_{0}$ falls away because the starting value is 0.
